Reading time
0 min
An innovative approach to the study of living organisms: from an individualistic to a holistic analysis
A paradigm shift in the study of living organisms. This is what was proposed in a study just published in Science by theHolobiont Biology Network, an international consortium that includes researchers from numerous institutions including the University of Padua, Penn State University, the University of Copenhagen, NTNU University Museum, the University of Pittsburgh and the National University of Colombia.

""
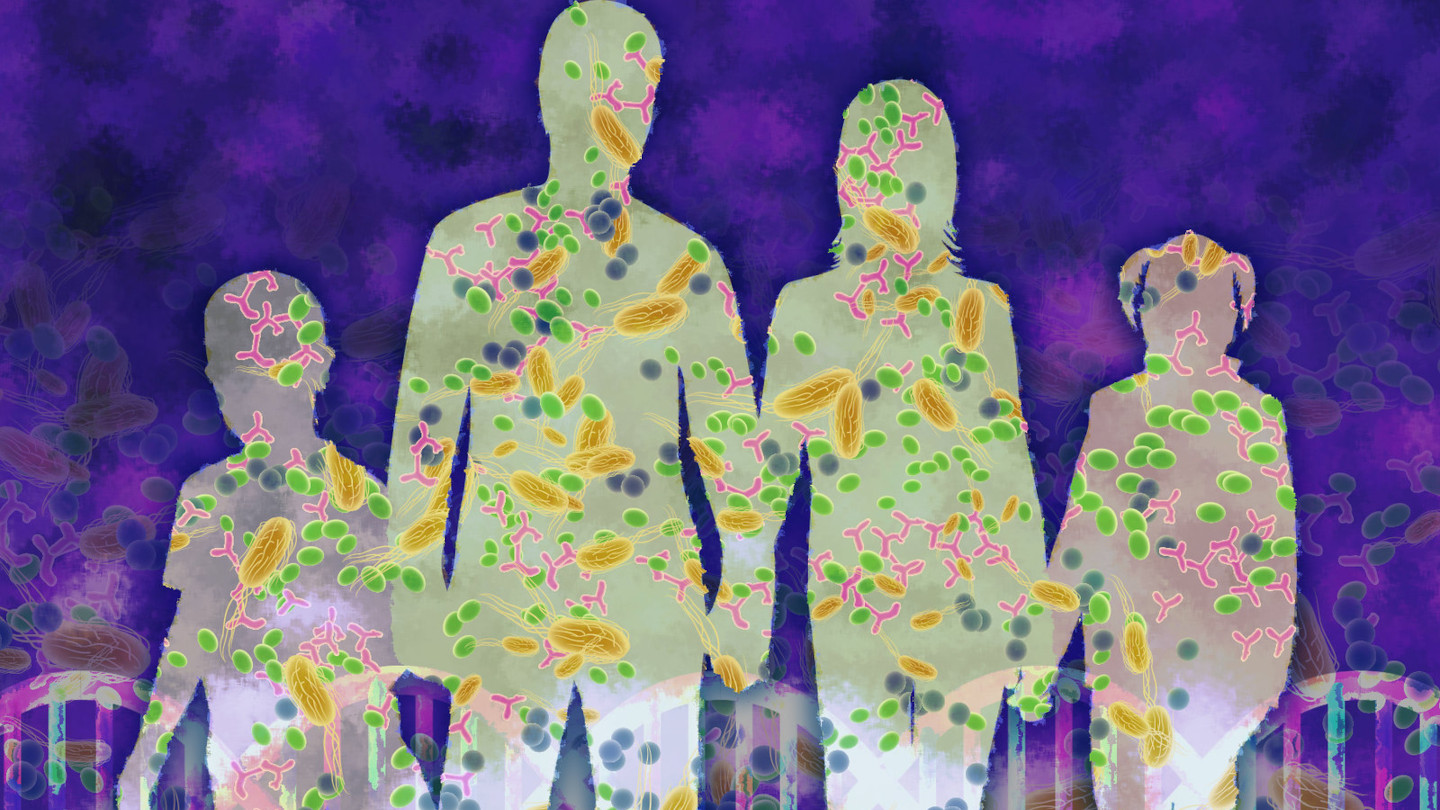
According to the authors of the study, the traditional approach that sees living organisms as stand-alone entities, separate from the environment, must be overcome in favor of a holistic approach, which considers the living organism together with all the microorganisms living in or around it. Such a whole is referred to as a holobiont.
""
The holobiont, more than an organism
A holobiont is a biological entity composed of several species, including the host (animal, plant or other organism) and its microbiome, which is the community of bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms that inhabit it.
Traditional biology has always considered organisms as autonomous entities, determined primarily by their genes. The new approach, on the other hand, emphasizes the interconnection between the host and its microbiome, recognizing the fundamental role that microorganisms play in host biology.
""
Hologenome surprises
Instead of looking only at the host genome, analyzing the hologenome, which includes both the host genome and that of its microbiota, provides a more complete and accurate view of the host’s biology.
The microbiome is crucial: it can influence the onset of several metabolic diseases, cholesterol or colon cancer risk, and even body mass index, as well as hip circumference in humans, insecticide resistance in wasps, or the vigor of hybrid plants.
""
Biodiversity as a web of relationships among organisms
On complex biological interactions depend not only the health and resilience of organisms, but also that of entire ecosystems. According to the study authors, it is also desirable to take a holistic approach in environmental sustainability and biodiversity maintenance.
Coral reefs are a typical example of an ecosystem hard hit by pollution and climate change. To counter these issues, probiotic bacteria capable of protecting corals and marine ecosystems are being tested. These microorganisms would be able to reverse bleaching and biodiversity loss.
Living organisms, the authors of the research argue, are connected by a dense network of relationships. The holistic approach proposed in the study shows how it is more effective to study each organism as a complex of relationships, rather than as a separate, stand-alone entity.
The journey goes on
Every story paves the way for the next: discover where biodiversity takes you